Iteration
What is iteration?
- Iteration is the process of doing something more than once (repeat), otherwise known as a loop
- A loop can be count controlled which means the code is repeated a fixed number of times
- A loop can also be condition controlled which means the code is repeated until a condition is met
- Three common loops are:
- **for loops **(count controlled)
- while loops (condition controlled)
- do while loops (condition controlled)
For Loops
- A
forloop is a count controlled loop that will repeat a fixed number of times. It provides a concise and structured way to perform repetitive tasks.
Syntax of a for loop
The syntax of a for loop consists of three main parts:
01 for i = x to y
02 // Code to be executed in each iteration
03 next i
- Initialisation: The initialisation is executed only once at the beginning of the loop. It is used to initialise a counter variable that controls the loop’s execution which is
iin this example - Range: The range that the count variable will increment through
- Increment/Decrement: The default is to increment by 1 each time unless specified
Pseudocode example
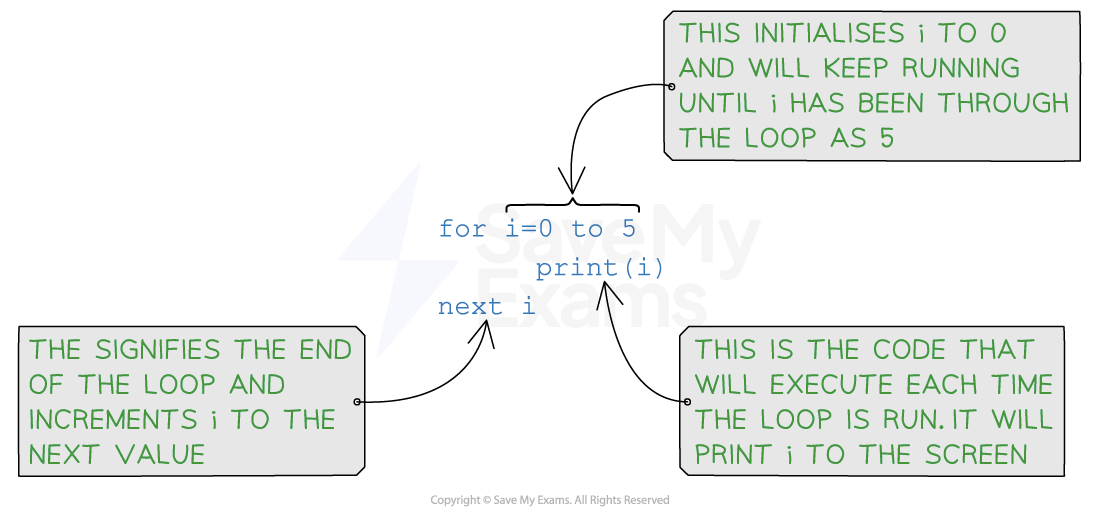 for loop example pseudocode
for loop example pseudocode
Python example
01 for i in range(0,6):
02 print i
In Python, the range specifies the numbers used in the loop. The final number (6 in this case) is 1 higher than the number we want to run the loop with.
Java example
01 for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
02 System.out.println(i);
03 }
Iterating over an array
Pseudocode example
 for loop iterating over an array and outputting each item
for loop iterating over an array and outputting each item
Python example
01 fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
02 for i in range(len(fruits)):
03 num = int(input("Enter a number: "))
04 numbers.append(num)
05 # Assume the first number is the largest
06 largest_number = numbers[0]
07 # Identifying the largest number
08 for num in numbers:
09 if num > largest_number:
10 largest_number = num
11 print("The largest number is:", largest_number)
Java example
01 String[] fruits = {"apple", "banana", "orange"};
02 for (int i = 0; i < fruits.length; i++) {
03 System.out.println(fruits[i]);
04 }
While Loops
- A
whileloop is a condition controlled loop that will repeat until a condition is met Whileloops provide a flexible and powerful way to handle situations where the number of iterations is unknown in advance
Syntax of a while loop
- The syntax of a
whileloop consists of a condition and a code block:
01 while condition
02 // Code to be executed as long as the condition is true
03 endwhile
- The condition is evaluated **before **each iteration. If the condition evaluates to
true, the code block is executed - If the condition evaluates to
false, the loop terminates.
Pseudocode example
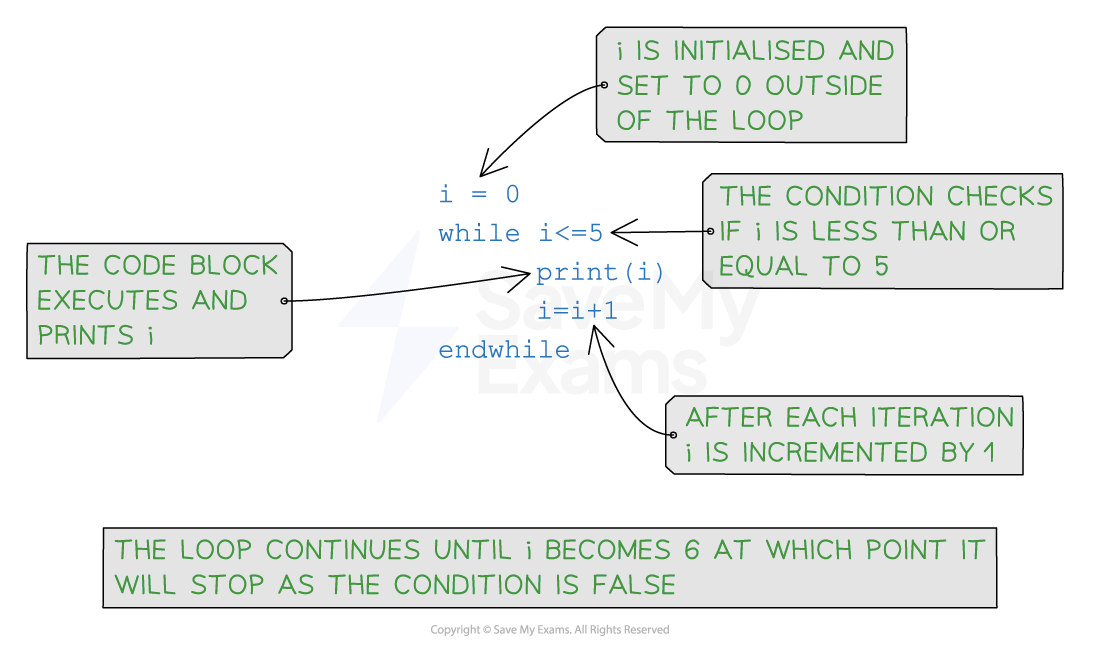 while loop example pseudocode
while loop example pseudocode
Python example
01 i = 0
02 while i <= 5:
03 print(i)
04 i = i + 1
Java example
01 int i = 0;
02 while (i <= 5) {
03 System.out.println(i);
04 i = i + 1;
05 }
Checking if the password is ‘secret’
Pseudocode example
 while loop checking if the password is correct
while loop checking if the password is correct
Python example
01 password = ""
02 while password != "secret":
03 password = input("What is the password? ")
Java example
01 import java.util.Scanner;
02 public class Main {
03 public static void main(String[] args) {
04 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
05 String password = "";
06 while (!password.equals("secret")) {
07 System.out.print("What is the password? ");
08 password = scanner.nextLine();
09 }
10 scanner.close();
11 }
12 }
Examiner Tips and Tricks
- Incrementing a variable can be done in different ways (depending on the language)
- For example:
- i= i + 1
- i + = 1
- i++
Worked Example
A simple Python program is shown below.
01 //Program to calculate the number of times a number goes into 100 02 03 count = 0 04 num = int(input("Enter a number")) 05 while (count*num)<=100 06 count=count+1 07 endwhile 08 count=count-1 //Take one off as gone over 09 print(str(num) + " goes into 100 " + str(count) + " times.")State the output of the program when the number 30 is entered.
[1]
How to answer this question:
- If 30 is entered this is saved in the variable
num- The
whileloop will run whilecount*numis less than or equal to 100countis 0, so 30 * 0 = 0- As there is a loop to iterate through it would be useful to produce a trace table to help us keep track of the value of the different variables
count num count * num 0 30 1 30 2 60 3 90 4 120 3
- The loop will repeat and when
countis 4,count*numis 120 which causes the condition to be false and the loop to stop- Count is decremented
- The statement which is printed is 30 goes into 100 3 times
Answer:
30 goes into 100 3 times.
Do While Loops
- A
do whileloop is another example of a condition controlled loop that will repeat until a condition is met. Do whileloops provide a variation of thewhileloop with a slightly different behaviour- The code within a
do whileloop will always run at least once, unlike awhileloop which may not run at all if the condition is already met
Syntax of a do while loop
- The syntax of a
do whileloop consists of a code block and a condition:
01 do
02 // Code to be executed at least once
03 until condition
- Code Block: The code block is executed first before evaluating the condition
- Condition: The condition is evaluated after executing the code block. If the condition evaluates to
false, the loop continues executing. If the condition evaluates totrue, the loop terminates
Pseudocode example
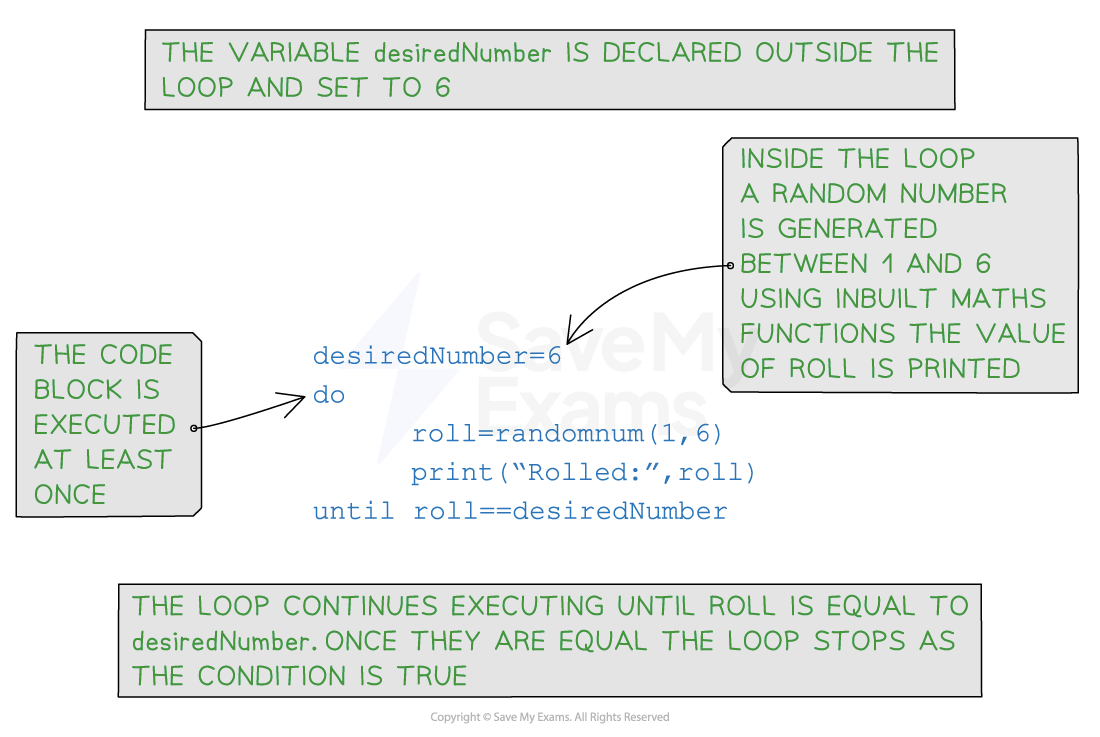 Do while example pseudocode
Do while example pseudocode
Python example
- It isn’t possible to use a do while loop in Python so the code would need to be written to use a while loop
01 import random
02 desired_number = 6
03 roll = 0
04 while roll != desired_number:
05 roll = random.randint(1, 6)
06 print("Rolled:", roll)
Java example
01 import java.util.Random;
02 public class Main {
03 public static void main(String[] args) {
04 Random random = new Random();
05 int desiredNumber = 6;
06 int roll;
07 do {
08 roll = random.nextInt(6) + 1;
09 System.out.println("Rolled: " + roll);
10 } while (roll != desiredNumber);
11 }
12 }
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You can use either a
whileloop or ado whileloop but don’t forget that ado whileloop will always run once before checking if the condition is true