What is Boolean logic?
- Boolean logic is used in computer science and electronics to make logical decisions
- Boolean operators are either TRUE or FALSE, often represented as 1 or 0
- Inputs and outputs are given letters to represent them
- To define Boolean logic we use special symbols to make writing expressions much easier
- Boolean algebra is easily confused with Boolean logic, but they are not the same
- Boolean logic refers to the principles of logic based on binary values
- Boolean algebra is a mathematical system used to manipulate Boolean values
Combination of Boolean operators
- Can be combined to form more complex expressions
- Use parentheses to clarify the order of operations
- Example: NOT (TRUE AND FALSE) = TRUE
Evaluating Boolean expressions
- There is a specific sequence for evaluating expressions with multiple operators just like in normal maths where BIDMAS applies
- Brackets come first then NOT then AND then OR
- Using brackets can alter the standard order of operations
- Expressions within brackets are evaluated first, following the same NOT, AND, OR precedence inside the brackets
- Example: NOT (TRUE AND FALSE) equals NOT FALSE, which equals TRUE
Logic Gates
- Logic gates are a visual way of representing a Boolean expression
- The logic gates covered in this course are:
- Conjunction (AND)
- Disjunction (OR)
- Negation (NOT)
- Exclusive disjunction (XOR)
Conjunction (AND)
| Operation | Circuit symbol | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Returns TRUE only if** both** inputs are TRUE TRUE AND TRUE = TRUE Otherwise = FALSE Next highest precedence after NOT Executes before OR operations |
Disjunction (OR)
| Operation | Circuit symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Returns TRUE if either input is TRUE TRUE OR FALSE = TRUE FALSE OR FALSE = FALSE Lowest precedence in Boolean expressions Executes after NOT and AND operations |
Negation (NOT)
| Symbol | Circuit symbol | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Inverts the input value NOT TRUE = FALSE NOT FALSE = TRUE Highest precedence in Boolean expressions Executes before AND and OR operations |
Exclusive Disjunction (XOR)
| Operation | Circuit symbol | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Outputs TRUE if the inputs are different Outputs FALSE if they are the same |
Truth Tables
- A tool used in logic and computer science to visualise the results of Boolean expressions
- They represent all possible inputs and the associated outputs for a given Boolean expression
Conjunction (AND)
| Circuit Symbol | A | B | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Disjunction (OR)
| Circuit Symbol | A | B | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Negation (NOT)
| Circuit Symbol | A | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 |
Exclusive Disjunction (XOR)
| Circuit Symbol | A | B | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Understanding the order of operations is crucial for correctly interpreting complex Boolean expressions
Misunderstanding the order can lead to incorrect results
Always use parentheses for clarity when combining multiple Boolean operations
Worked Example
Daniel is an engineer. He has created the following logic circuit as shown
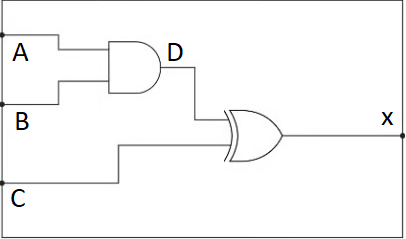
Complete the truth table below for the logic circuit shown
| A | B | C | D | X |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
[4 marks]
Example answer that gets full marks:
| A | B | C | Calculating D | D | Calculating X | X | Mark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | D is the result of A AND B | 0 | X is the result of D XOR C | 0 | 1 Mark |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | D is the result of A AND B | 0 | X is the result of D XOR C | 1 | 1 Mark |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | D is the result of A AND B | 0 | X is the result of D XOR C | 0 | 1 Mark |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | D is the result of A AND B | 0 | X is the result of D XOR C | 1 | 1 Mark |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | D is the result of A AND B | 0 | X is the result of D XOR C | 0 | 1 Mark |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | D is the result of A AND B | 0 | X is the result of D XOR C | 1 | 1 Mark |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | D is the result of A AND B | 1 | X is the result of D XOR C | 1 | 1 Mark |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | D is the result of A AND B | 1 | X is the result of D XOR C | 0 | 1 Mark |