Queues
What is a queue?
- A queue is a First in First out (FIFO) data structure
- Items are added to the end of the queue and removed from the front
- A queue has a back (tail) pointer and a front (head) pointer
- Much the same as with a stack, an attempt to enqueue an item when the queue is full is called a queue overflow. Similarly, trying to dequeue an item from an empty queue is called a queue underflow.
- A queue can be static or dynamic
- There are three types of queues
- Linear Queue
- Circular Queue
- Priority Queue
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
enQueue(value) | Adding an element to the back of the queue |
deQueue() | Returning an element from the front of the queue |
peek() | Return the value of the item from the front of the queue without removing it from the queue |
isEmpty() | Check whether the queue is empty |
isFull() | Check whether the queue is full (if the size has a constraint) |
- Stacks use a pointer which points to the top of the stack, where the next piece of data will be added (pushed) or the current piece of data can be removed (popped)
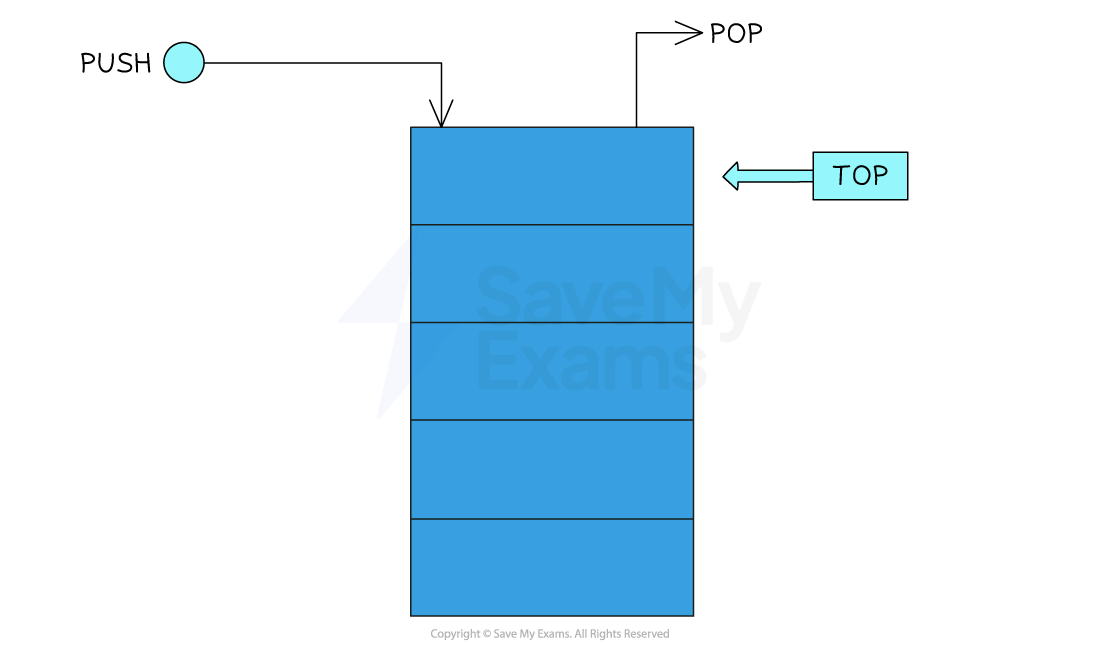 Push visual example
Push visual example
Linear Queues
What are linear queues?
- A linear queue is a data structure that consists of an array.
- Items are added to the next available space in the queue starting from the front
- Items are then removed from the front of the queue
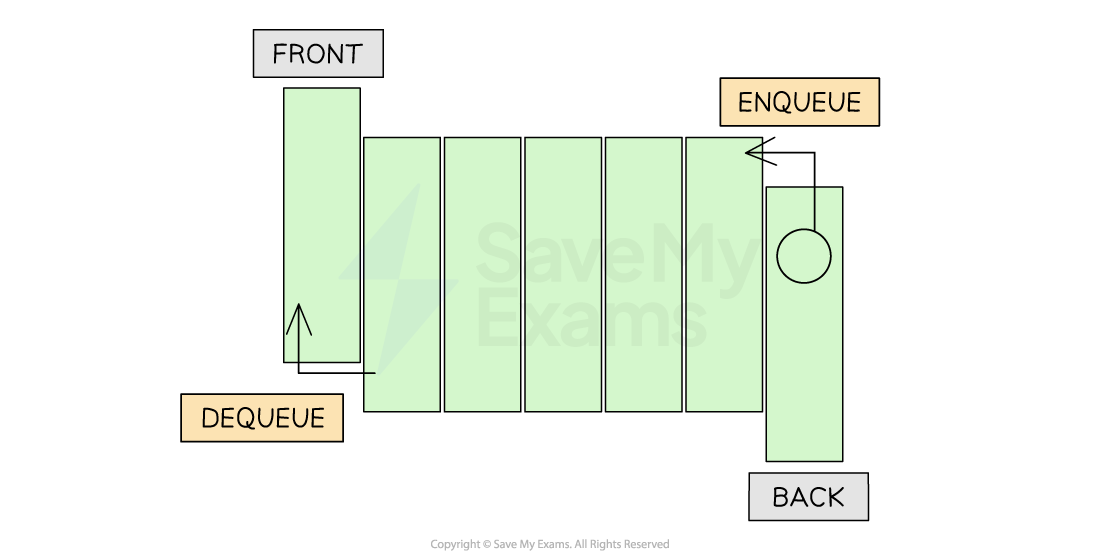 Linear Queue
Linear Queue
Enqueue data
- Before adding an item to the queue you need to check that the queue is not full
- If the end of the array has not been reached, the rear index pointer is incremented and the new item is added to the queue
- In the example below, you can see the queue as the data Adam, Brian and Linda are enqueued.
(Images for enqueue Adam, Brian, Linda as in HTML)
Dequeue data
- Before removing an item from the queue, you need to make sure that the queue is not empty
- If the queue is not empty the item at the front of the queue is returned and the front is incremented by 1
- In the example below, you can see the queue as the data Adam is dequeued
(Dequeue Adam image)
Circular Queues
What are circular queues?
- In A Level Computer Science, a circular queue is a static array that has a fixed capacity
- It means that as you add items to the queue you will eventually reach the end of the array
- When items are dequeued, space is freed up at the start of the array
- It would take time to move items up to the start of the array to free up space at the end, so a Circular queue (or circular buffer) is implemented
- It reuses empty slots at the front of the array that are caused when items are dequeued
- As items are enqueued and the rear index pointer reaches the last position of the array, it wraps around to point to the start of the array as long as it isn’t full
- When items are dequeued the front index pointer will wrap around until it passes the rear index points which would show the queue is empty
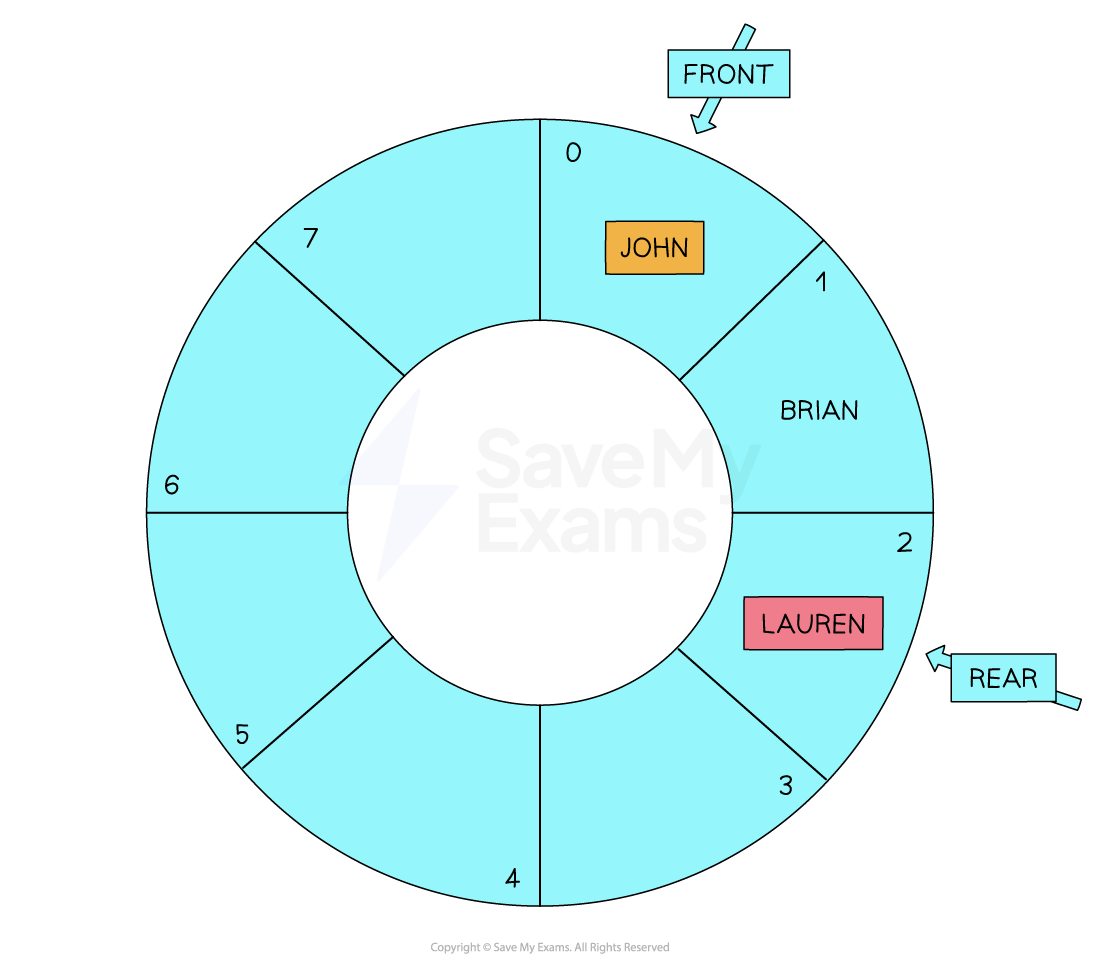 Circular Queue
Circular Queue
Enqueue data
- Before adding an item to the circular queue you need to check that the array is not full
- It will be full if the next position to be used is already occupied by the item at the front of the queue
- If the queue is not full then the rear index pointer must be adjusted to reference the next free position so that the new item can be added
( enqueue Lauren images )
Dequeue data
- Before removing an item from the queue, you need to make sure that the queue is not empty
- If the queue is not empty the item at the front of the queue is returned
- If this is the only item that was in the queue the rear and front pointers are reset, otherwise the pointer moves to reference the next item in the queue
( dequeue Adam images )
TIP
When asked to display a queue visually, make sure that you also identify the position of the front and rear pointers.
EXAMPLE
Stacks and queues are both data structures.
The queue has the subprograms enqueue and dequeue. The subprogram ‘enqueue’ is used to add items to the queue and the subprogram ‘dequeue’ removes items from the queue.
Use the following diagram to show the queue after the operations: enqueue(“A”), dequeue(), enqueue(“B”), dequeue(), dequeue()
(Table with colours as in HTML, then the steps with tables)
The final answer with table.