- Nesting is putting one block of code within another
- This is commonly done with
ifstatements and loops - Nested
ifstatements refer to the practice of including one or more conditional statements inside the block of another conditional statement - These nested structures allow you to create more complex decision-making logic by evaluating multiple conditions and handling various scenarios within your code
- Nested loops refer to the practice of including one or more loops inside the block of another loop
- These nested structures allow you to iterate over multiple sets of data and create more complex patterns of repetition within your code
Nested If statements in JavaScript
Ifstatements can be nested within each other to handle more intricate conditions and decision-making:
 Nested if statement in JavaScript
Nested if statement in JavaScript
Nested loops in JavaScript
- The syntax of nested loops involves placing one loop (
forloop,whileloop, etc.) inside the block of another loop:
for (let i = 0; i < outerArray.length; i++) {
// Code block for outer loop
for (let j = 0; j < innerArray.length; j++) {
// Code block for inner loop
// More nested loops if needed
}
// More code after inner loop
}
Example: nested for loops
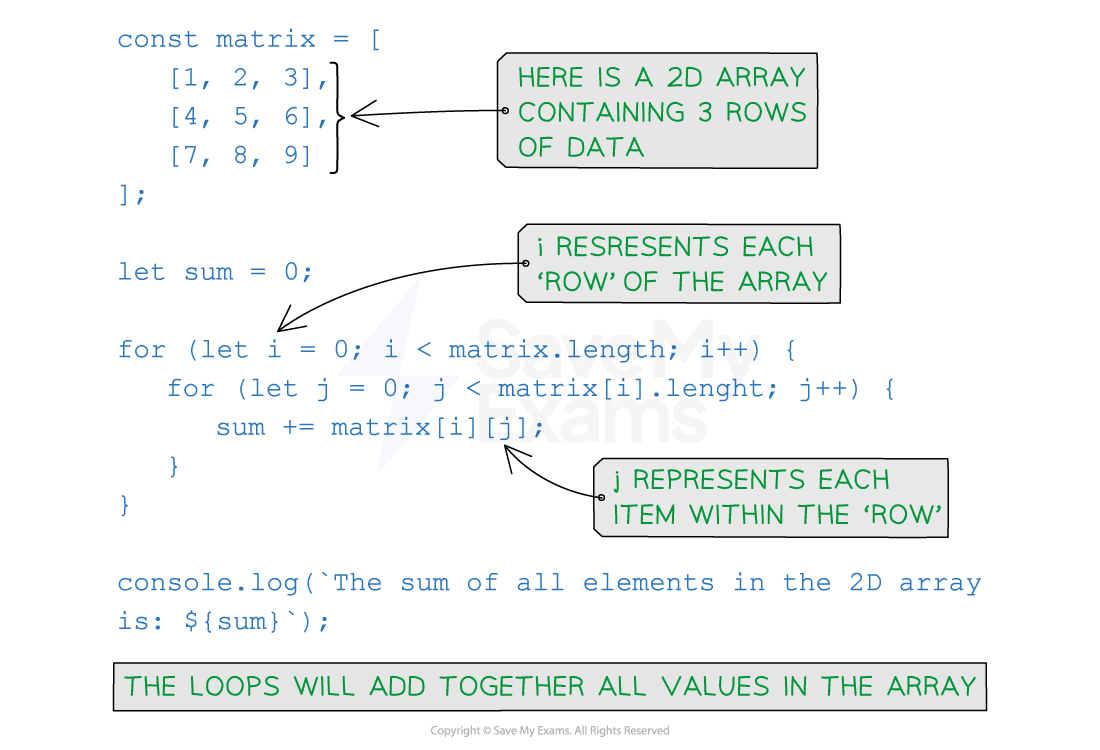 Nested for loop in JavaScript showing a 2D array with each item in the array being added together to find the sum of the whole array
Nested for loop in JavaScript showing a 2D array with each item in the array being added together to find the sum of the whole array
- After the first iteration
sum=1as it’s only added the 1st element which is 1 - After the 2nd iteration
sum=3as it’s added the 2nd element (2) to 1 - After the 3rd iteration
sum=6as it’s added the 3rd element (3) to the 1 and 2 - After the 4th iteration
sum=10as it’s added the 4th element (4) to the 1, 2 and 3 - The algorithm continues working its way through the rest of the 2nd row and then moves on to the 3rd
Example: nested while loops
- This code below does the same as the code above but utilises
whileloops rather thanforloops:
const matrix = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]
];
let i = 0;
while (i < matrix.length) {
let j = 0;
while (j < matrix[i].length) {
console.log(matrix[i][j]);
j++;
}
i++;
}
Examiner Tips and Tricks
- If you need to check or work out how many times an inner loop is run, multiply the number of outer loop iterations by the number of inner loop iterations. E.g.
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
console.log(i * j);
}
}
- The outer loop runs 3 times and the inner loop will run 5 times. To find out the total number of times the inner loop will run, multiply 3 by 5 = 15