- A
forloop is a control flow statement that allows a block of code to repeatedly execute for a specified number of iterations - It provides a concise and structured way to perform repetitive tasks.
Syntax of a for loop
- The syntax of a
forloop consists of three main parts:
for (initialisation; condition; increment/decrement) {
// Code to be executed in each iteration
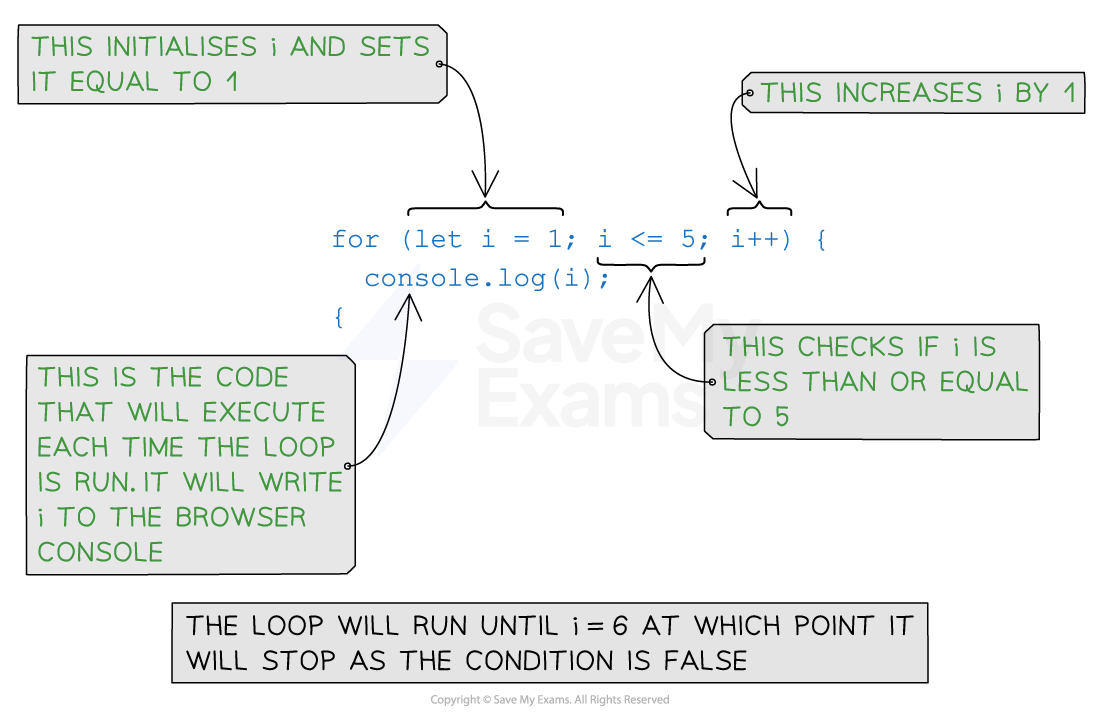
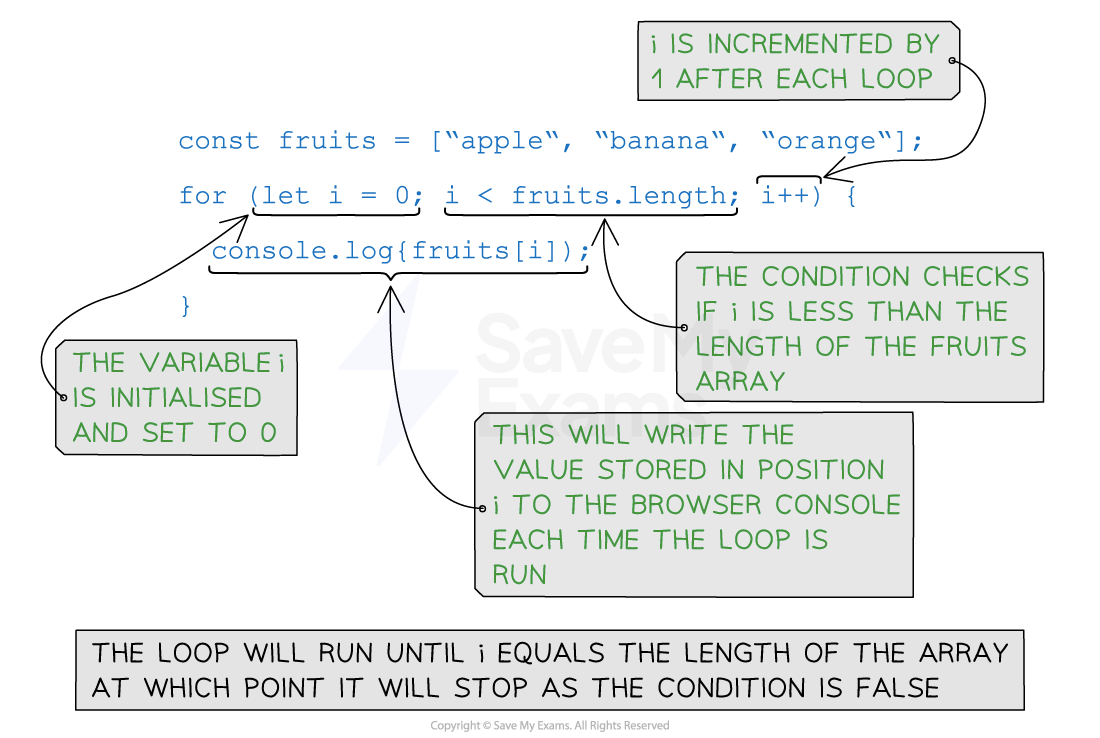
}- Initialisation: The initialisation is executed only once at the beginning of the loop. It is used to initialise a counter variable that controls the loop’s execution
- Condition: The condition is evaluated before each iteration. If the condition evaluates to true, the loop continues executing the code block. If the condition evaluates to false, the loop terminates
- Increment/Decrement: The increment or decrement statement is executed at the end of each iteration, updating the counter variable to control the loop’s progress
Example 1: Counting from 1 to 5
Example 2: Iterating over an array
Examiner Tips and Tricks
- You might have seen
i=i+1ori+=1for incrementing by 1. This is the same asi++in JavaScript
’For in’ loops in JavaScript
- The
for inthe loop iterates through the items in a data structure like a list or array
const fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'grape'];
for (let index in fruits) {
console.log('Index: ' + index + ', Value: ' + fruits[index]);
}- The list
fruitscontains four items:'apple','banana','orange', and'grape' - The
for...inthe loop iterates over each index of thefruitslist - In each iteration, the
indexthe variable is assigned the current index value - Inside the loop, we use
fruits[index]to access the value associated with the current index - The loop executes the code block, which outputs the index and value of each item in the list to the browser