What is compilation?
- Compilation is a process that translates a program written in a high-level programming language into machine code
- Only machine code can be directly executed by a computer
- There are four stages involved in this process:
- Lexical Analysis
- Syntax Analysis
- Code Generation
- Optimisation
Lexical analysis
-
Lexical analysis means studying the words or vocabulary of a language
-
This stage involves identifying lexical ‘tokens’ in the code
-
Tokens represent small meaningful units in the programming language, such as:
- Keywords
- var, const, function, for, while, if
- Identifiers
- Variable names, function names
- Operators
- ’+’, ’++’, ’-’, ’*’
- Separators
- ’,’, ’;’, ’{’, ’}’, ’(’, ’)’
- Keywords
-
During this stage, unnecessary elements like comments and whitespace are ignored
-
For example, if the following code is being compiled:
var x = function(x,y) {
if(x>2) {
return x*y;
}
return x+y;
}- The result of lexical analysis is a token table
| Token | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | var | Keyword |
| 2 | x | Identifier |
| 3 | = | Operator |
| 4 | function | Keyword |
| 5 | ( | Separator |
| 6 | x | Identifier |
| 7 | , | Separators |
| 8 | y | Identifier |
| 9 | ) | Separator |
| 10 | { | Separator |
| 11 | return | Keyword |
| 12 | x | Identifier |
| 13 | * | Operator |
| 14 | y | Identifier |
| 15 | ; | Separator |
| 16 | } | Separator |
Syntax analysis
- Now that tokens have been identified, syntax analysis makes sure they all adhere to the syntax rules of the programming language
- A symbol, e.g. ’$’ could be a valid token but not a valid character according to particular programming languages
- The dollar symbol would be flagged as breaking the syntax rules
- Other syntax errors programmers commonly make include mismatched parentheses or missing semicolons
- If the code passes the syntax analysis, the compiler can create an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST)
- An AST is a graph-based representation of the code being compiled
- An AST is an efficient way to represent the code for the next step
Example abstract syntax tree
- For the same code as above, the following abstract syntax tree can be created
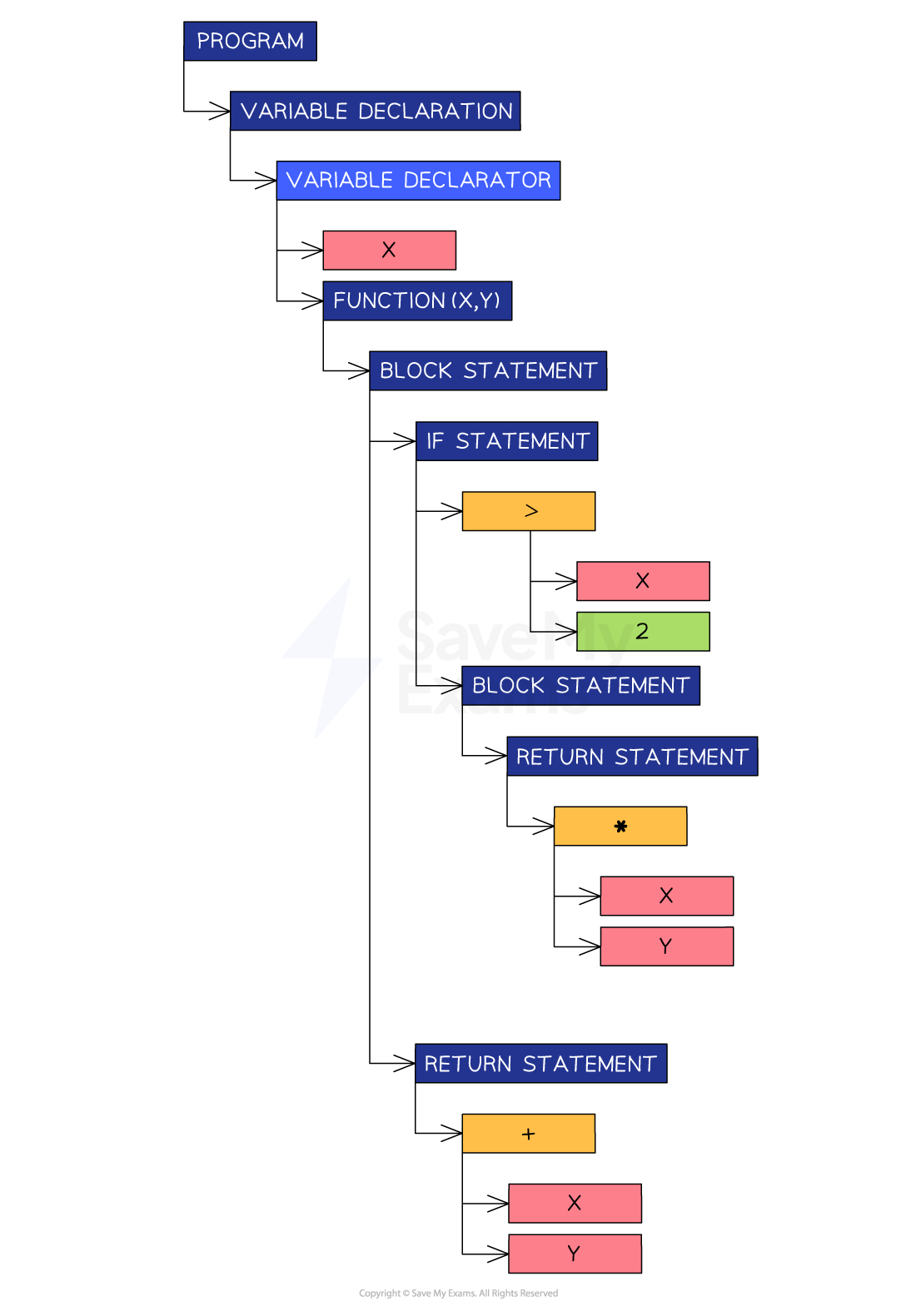 Abstract syntax tree
Abstract syntax tree
Code generation
- This step takes the AST and traverses it to generate object code that can be executed by the computer
Optimisation
- This step modifies the code to make it more efficient without changing its functionality
- This is important to attempt because it reduces the memory required to run the code, which leads to faster execution
- A common optimisation action is removing duplicate code
- If an ‘add’ function is written twice in the source code, a sophisticated compiler will notice this and include it only once in the object code
Summary of Compilation Stages
- Lexical Analysis
- The process of converting lexemes in the source code into a series of tokens
- Converts source code into tokens, removing whitespace and comments. Generates a symbol table for tracking variables and subroutines
- Syntax Analysis
- Validates the syntactical structure of tokens received from the lexical analyser
- Creates an abstract syntax tree (AST) from tokens. Reports syntax errors if tokens break language rules
- Code Generation
- Transforms the abstract syntax tree into object code for the target system
- Code Optimisation
- Refines the final code to reduce execution speed and improve memory efficiency
Worked Example
Imogen is writing application software for her company and is ready to compile it.
const celsius = (fahrenheit) => { return (5/9) * (fahrenheit-32); }Referring to the example above, explain what happens during Lexical Analysis.
[2]
How to answer this question:
- Recall the purpose of lexical analysis and what it aims to produce
- Recall the different types of tokens that can be identified in the code
- Use examples from the code block to write your answer
Answer:
Answer that gets full marks: ‘Lexical analysis’ breaks the code into tokens, ignoring whitespace and comments. Tokens are identified by their type:
- keyword: ‘return’
- operator: ’*’, ’-’
- identifier: celsius, fahrenheit
- delimiter: ’;’, ’(’, ’)’ etc
When all tokens have been identified, a token table is produced for the next step in the compilation.
Acceptable answers you could have given instead:
The compiler will look at all the lexical tokens in the code e.g. ‘fahrenheit’ is an identifier, ‘return’ is a keyword. All the tokens are placed into a tokens table for the next step.
Worked Example
State the name of the stage of compilation that directly follows Lexical Analysis.
[1]
Answer:
Answer that gets full marks: Syntax analysis.